Sodium Borohydride (NaBH4)
Sodium borohydride (NaBH4) is a white, crystalline solid known for its critical role as a reducing agent in various organic transformations. Boasting the formula NaBH4, this compound is composed of sodium ions (Na+) and borohydride ions (BH4-). The borohydride ion carries four hydride (H-) ions, which are the source of its reducing power.

Chemical Properties
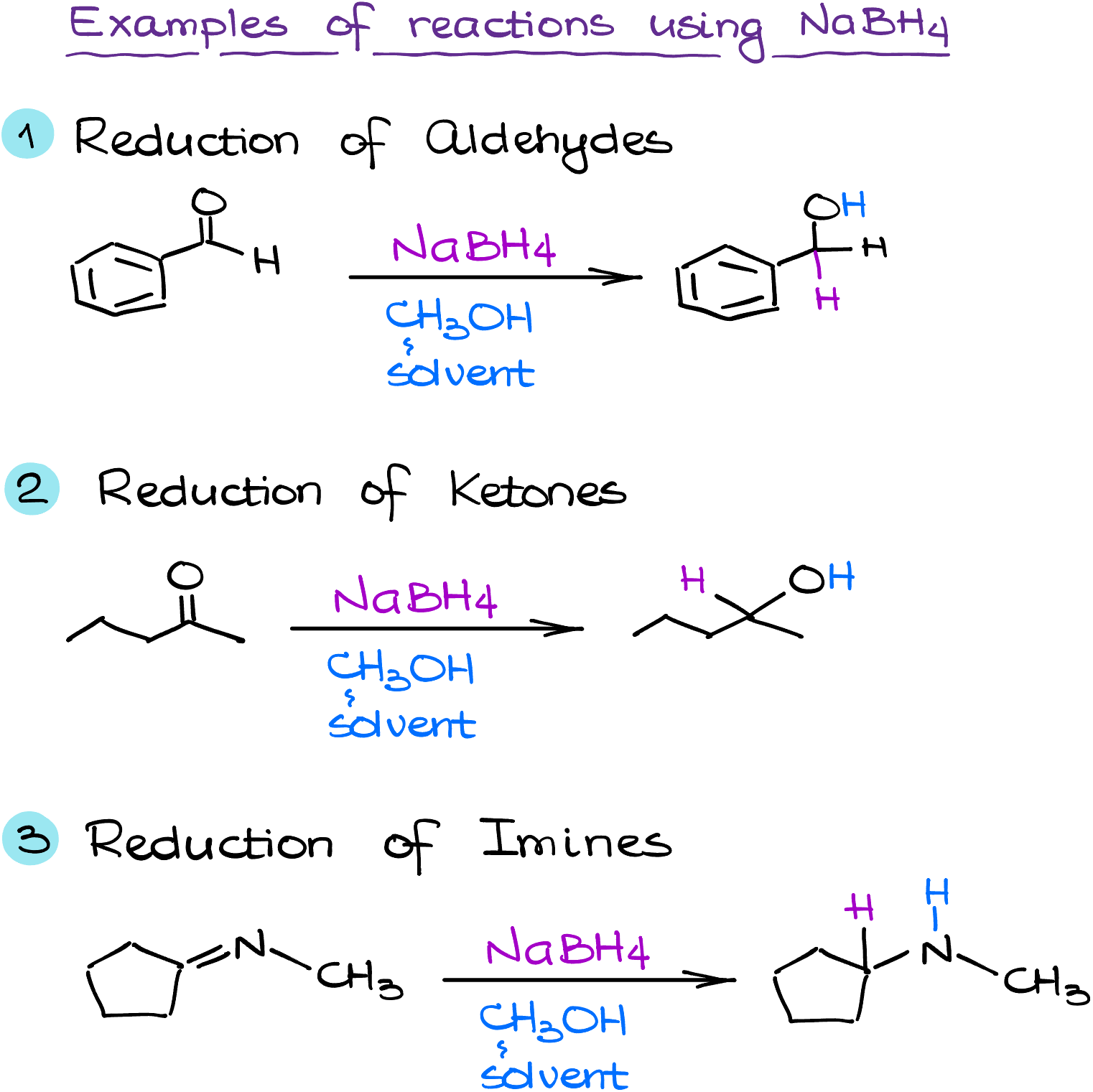
Chemically, sodium borohydride is a selective reducing agent. It primarily reduces carbonyl groups (C=O), such as those found in aldehydes and ketones, converting them to primary and secondary alcohols, respectively. Importantly, NaBH4 performs this reduction under mild conditions, which makes it possible to reduce a carbonyl group in the presence of other functional groups without disturbing them. This selectivity and mildness distinguish NaBH4 from other reducing agents and render it indispensable for certain synthetic tasks.
Safety Information
However, sodium borohydride is not without its safety concerns. It is highly reactive with water and can liberate hydrogen gas, a flammable substance, upon contact with moisture. Therefore, it should always be handled under dry conditions. Sodium borohydride can also cause skin and eye irritation. Always use appropriate personal protective equipment, work in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood, and handle with care to avoid accidental exposure.
Sodium borohydride, while a hazardous chemical, is a critical tool in the field of organic synthesis. Its mild and selective reducing properties make it a reliable reagent for various reduction reactions, enabling the transformation of simple molecules into complex structures. As with all reagents, careful handling and understanding of its properties are essential for safe and effective use.

excellent content
thank you so much.